|
|
What are explicit variants ? |
|
Explicit variants are one of two ways of representing variants in OptiLine, the other being the implicit variant representation by means of a BOM (Bill Of Materials) with possible product models. With explicit variants, each
of the possible variants of the product being assembled on the line
is explicitly listed, together with all operations being present for
each of the variants. One of advantages of explicit variants is that
it is possible to know exactly what are the possible combinations of
operations for any variant. That makes it possible to compute workstation
peak times and take them
into account in the automatic balancing
optimization. A workstation peak time is the time it takes to complete
all the operations assigned to a workstation, whatever the variant being
assembled at the station. Explicit variants are easily
visualized in the Operations
Tab in variant mode, activated by the Variant
navigator. For instance, showing the fuel model of the car would
yield the following figure, where the "Mount Diesel Engine"
operation is struck out, because that operation is absent from that
variant (it only appears in the fuel model). |
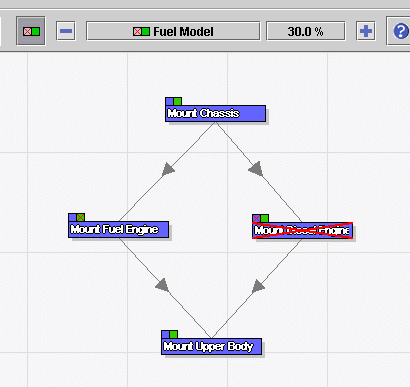
Showing a variant in the precedence graph
|
The list of explicit variants is easily edited in the Edit Variant Dialog box. |